What are Marine Animals?
Before knowing about corals and types of corals , let’s know about marine animals. Marine animals are all the animals that live in the ocean. They include fish, crustaceans, cephalopods, and other marine organisms. There is a wide variety of these creatures living in different habitats around the world. Unlike terrestrial animals, marine animals don’t have to worry about land predators and can explore the depths of the water. Some of them are mammals, Some are invertebrates, Others are fish. Marine creatures have adapted to life in saltwater and usually live near or on the ocean floor.
Some fascinating facts about Marine Animals:
– A shark can go without food for six months
– Almost 1/3 of all marine animals are in danger of extinction
What are Corals?
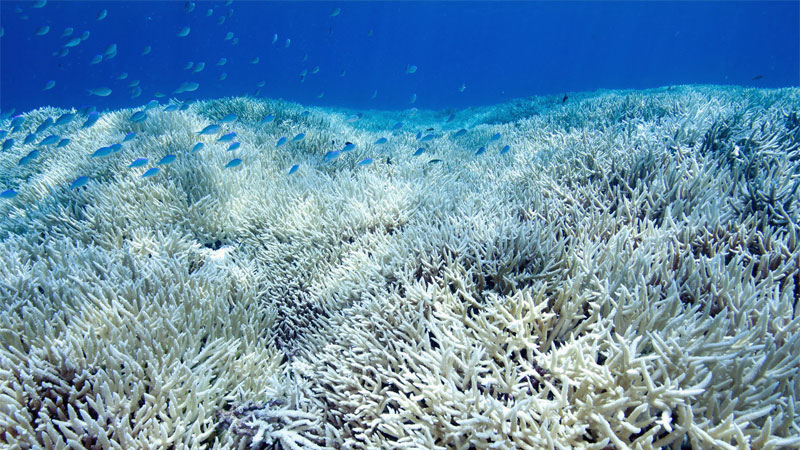
Corals are animals that live in the oceans near the surface. It is a type of sea animal made up of polyps that have stony outer skeletons. They come in all shapes and sizes, with some having tentacles and some lacking them.
They get their name from their resemblance to the beautiful bright colors of tropical coral reefs. There are many different types of corals, but they all have one thing in common: hard outer skeletons that protect soft living tissue inside. They are grouped into three main categories – hard corals, soft corals, and black corals.
Are corals dangerous for humans?
Corals can be found in many different environments, but they are not all dangerous to humans. Some corals can be a danger if they get near the skin, while other corals are harmless. It is important to note that corals do have the potential to release potent chemicals into the water and air around them, which could be harmful to people in close proximity.
There are three main categories of corals: hard coral, soft coral, and branching coral. Hard and branching corals can release stingers and toxins that will affect the human body if touched. Soft corals do not release any toxins or stingers that could harm humans, but it does have microscopic razor-sharp edges that cause irritation when touched.
What are the types of corals?
Corals can be categorized into three types, hard coral, soft corals and branching corals.
- Hard corals: Hard corals have skeletons made of calcium carbonate and cover themselves with mucus that is secreted from their epidermis layer. This helps to filter out small particles from water, which they eat and protects them from other animals or predators. Hard corals receive their calcium carbonate from the seawater that surrounds them which makes them much more durable than their softer counterparts who require more care to survive.
- Soft corals: Soft corals are very flexible because they don’t have a hard skeleton as hard corals do. Furthermore, soft corals don’t generate their own calcium carbonate so they often come from food sources and need to stay moist at all times to survive. The soft corals are not part of the animal kingdom.
- Branching Corals: A branching coral is a coral that branches out from a single, central point. We often see this form of coral in the shallow waters near a reef. It branches often and has many points where new growths can start. It is a type of stony coral that has branches that are flat and unbranched. This type of coral is found in shallow water up to 16 feet deep.
On what basis the types of corals can be differentiated?
This section will help people who want to know on what basis the types of corals can be differentiated.
Different types of corals can be differentiated on the basis of their physical traits, habitat and reproductive strategy.
- On the basis of Physical traits:To differentiate between these types of physical traits, soft corals are usually tree-like with an airy tissue made up of tiny cells which makes them feel spongy to the touch.
Harder ones which cannot be manipulated as easily due to their solid structure might feel slimier in comparison to any other type.
Branching coral is best identified by its appearance – they have branches that connect from one end of their body to another and may have multiple openings for water intake with some species having a more pronounced crown at their top.
- On the basis of Habitat:The corals are not only different in terms of their physical appearance but also in terms of the environment they live in.
Soft corals are those that live on the outside edges of the reef and in areas where there is ample water flow.
When it comes to habitat, branching corals are restricted to harsh environments such as at the edge of a cliff or on a rock formation.
Hard corals thrive when there is plenty of sunlight and soft corals do better in shallow waters.
- On the basis of reproductive strategy:Hard corals are hermaphrodites, meaning that they are both male and female and can produce eggs and sperm.
Soft corals are not hermaphrodites as they are either male or female and require partners to reproduce. Soft corals release their eggs in one go, in the hope that they will be fertilized by another soft coral’s sperm.
Branching corals release their eggs through an opening near their base of attachment on the reef. The parents then guard these clusters of eggs until they hatch – typically in about 6 weeks.
For more blogs: Andreas25
Conclusion on Corals
Corals are slowly disappearing around the world. Many factors contribute to the fact that these creatures are slowly vanishing. But with our help, we can change their fate. Coral reefs play a vital role in our planet’s ecosystem and without them, we face a world without beautiful marine life. Therefore, it is important to take care of them and preserve them as they keep us alive.
We need to come together as one global unit to combat the issue of coral reefs not being sustainable anymore because if we don’t, who will?